How AI Adapts to Personality Types in Real Time
How AI reads language and behavior to identify personality traits and adjust tone, complexity, and style in real time to improve engagement and teamwork.

How AI Adapts to Personality Types in Real Time
AI systems now adjust their communication style based on personality traits, enhancing interactions in real time. By analyzing text, tone, and behavior, they identify traits like extraversion and conscientiousness using models like the Big Five. This approach boosts engagement, workplace productivity, and user satisfaction. Key advancements include:
- Real-Time Adaptation: AI modifies tone, complexity, and style during interactions based on user behavior.
- High Precision: Tools like PsychAdapter achieve 94.5% accuracy in matching personality traits.
- Workplace Benefits: Teams using AI see fewer conflicts, reduced meeting times, and better collaboration.
- Coaching Improvements: AI offers tailored insights for personal growth and professional development.
These systems rely on feedback loops, multimodal data, and reinforcement learning to refine their accuracy and responsiveness. Businesses using personality-driven AI report higher engagement and productivity, while privacy-focused tools ensure secure user data handling. The future of AI lies in deeper emotional understanding and proactive assistance.
How AI Identifies Personality Types
AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to dig into the way people write - examining word choice, sentence patterns, and emotional tone - to uncover personality traits. While the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) remains popular, AI often relies on frameworks like the Big Five Personality Traits because they’re more grounded in research and proven reliable.
Recent developments highlight the accuracy of AI in this area. For example, PsychAdapter, a model fine-tuned on 850,000 Facebook posts, correctly matched personality traits with an impressive 94.5% accuracy[2]. Similarly, GPT-4 was able to classify 76% of MBTI types by analyzing just 50 tweets[10]. These results showcase how AI uses text analysis as a starting point, building on it with advanced techniques to refine its understanding of personality.
AI and Linguistic Markers
The way people express themselves often reveals a lot about their personality. For instance:
- Extraverts tend to use upbeat, social words like “friends” and “excited.”
- Agreeable individuals lean toward terms like “family” and “love,” reflecting their communal focus.
- Neurotic traits show up in language tied to anxiety or sadness.
- Conscientious people often use achievement-oriented language[7].
Advanced models like PsychAdapter take this a step further. Instead of just sorting people into categories, they assign continuous numerical scores to personality traits, offering a more detailed and realistic picture. These updates are efficient too, adding less than 0.5% to a model’s parameters while influencing text generation at every level[2]. Research suggests this training-based approach produces more authentic personality insights compared to simpler methods like surface-level prompting, which can lead to exaggerated or overly simplistic personality "caricatures"[7]. Beyond just analyzing text, AI also incorporates behavioral signals to paint a fuller picture of personality.
Behavioral Signal Processing in AI
AI doesn’t stop at text - it also interprets non-verbal cues like facial expressions, tone of voice, and gestures to create richer personality profiles[9]. Engaging users with targeted questions about their personality further improves the accuracy of its predictions. For example, when GPT-4 was prompted to gather personality insights through open-ended interactions, it achieved a mean correlation of r = 0.443, reflecting its ability to capture nuanced traits[8].
The integration of multimodal data - combining text, visuals, and audio - is a growing trend in this field. Deep learning methods now account for over 40% of research into personality recognition, with convolutional neural networks contributing about 15% of that work[9]. These systems are also incredibly consistent, with reliability scores ranging from 0.97 to 0.99, far surpassing the 0.79 to 0.89 range typical of human self-assessments[11]. Together, these advancements allow AI to build dynamic, real-time personality profiles that are more comprehensive than ever before.
How AI Adjusts Communication Strategies in Real Time
Static vs Adaptive AI: Key Differences in Performance and Capabilities
When AI systems identify personality traits, they instantly adapt their communication style. These systems don’t just analyze personality - they actively modify their responses in real time. By using behavioral tracking, reinforcement learning, and structural tweaks, AI treats personality as a fluid input rather than a fixed label. This adaptability enables more tailored and responsive interactions.
Take HumAIne-chatbot as an example. It monitors subtle cues like typing speed and response time during user interactions. A "Prompt Manager" refines the AI’s instructions on the fly, adjusting vocabulary, tone, and technical complexity. Whether the user prefers a professional or conversational style, the system adapts based on their expertise and emotional state[12]. This is powered by Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), a reinforcement learning algorithm that maps user behavior to specific response strategies.
This approach reflects a growing focus on "Affective RL" - an effort to optimize AI for both accuracy and emotional sensitivity[6]. Systems like Profile-LLM take it further, using Optimization by PROmpting (OPRO) to fine-tune personality traits. Developers can pause the process to adjust the "intensity" of traits, treating personality as a spectrum rather than a binary setting[1].
On a technical level, systems like PsychAdapter tweak transformer architectures to incorporate continuous personality scores. These adjustments allow the AI to generate text that aligns with specific personality traits. In fact, expert evaluations found that PsychAdapter achieved a 94.5% match between generated text and intended personality traits[2].
Continuous Learning and Feedback Loops
The secret to adaptive AI lies in its ability to learn from every interaction. Unlike static models that rely on fixed training data, adaptive systems refine their strategies through constant feedback. For instance, the DEEPER framework optimizes user personas over multiple interactions. After just four update cycles, prediction errors in user behavior dropped by 32.2%[13].
This refinement happens on multiple levels. AI systems gather explicit feedback, like user ratings and questionnaires, while also analyzing implicit behavioral signals. In 2025, researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering introduced a "virtual humans" system capable of adjusting its extroversion levels during live interactions. Presented at the IVA 2025 conference, the study showed how these empathetic AI agents could mirror user personalities in real time. This approach proved especially effective in scenarios like salary negotiations and mental health support. As Professor Jonathan Gratch explained:
"You might imagine another step is to create these agents that adapt to you as they learn more about you over time. They can better align themselves, not just in terms of your needs, but also the way you want those needs communicated."[4]
Another striking example comes from Stanford University, where researchers led by Joon Sung Park simulated the personalities of 1,052 individuals. They used a large language model paired with an AI interviewer to conduct two-hour interviews, capturing participants’ beliefs and quirks. The resulting generative agents matched survey answers with 85% accuracy and personality test results with an 80% correlation[17]. This project demonstrated how life-story interviews can help AI mirror human decision-making patterns with precision.
Adaptive AI also excels at self-correction. By analyzing past interactions, these systems avoid repeating mistakes[15]. Some even use large language models to review transcripts from the perspective of experts, such as social psychologists. This allows the AI to create a deeper understanding of a user’s personality, improving its responses over time[17].
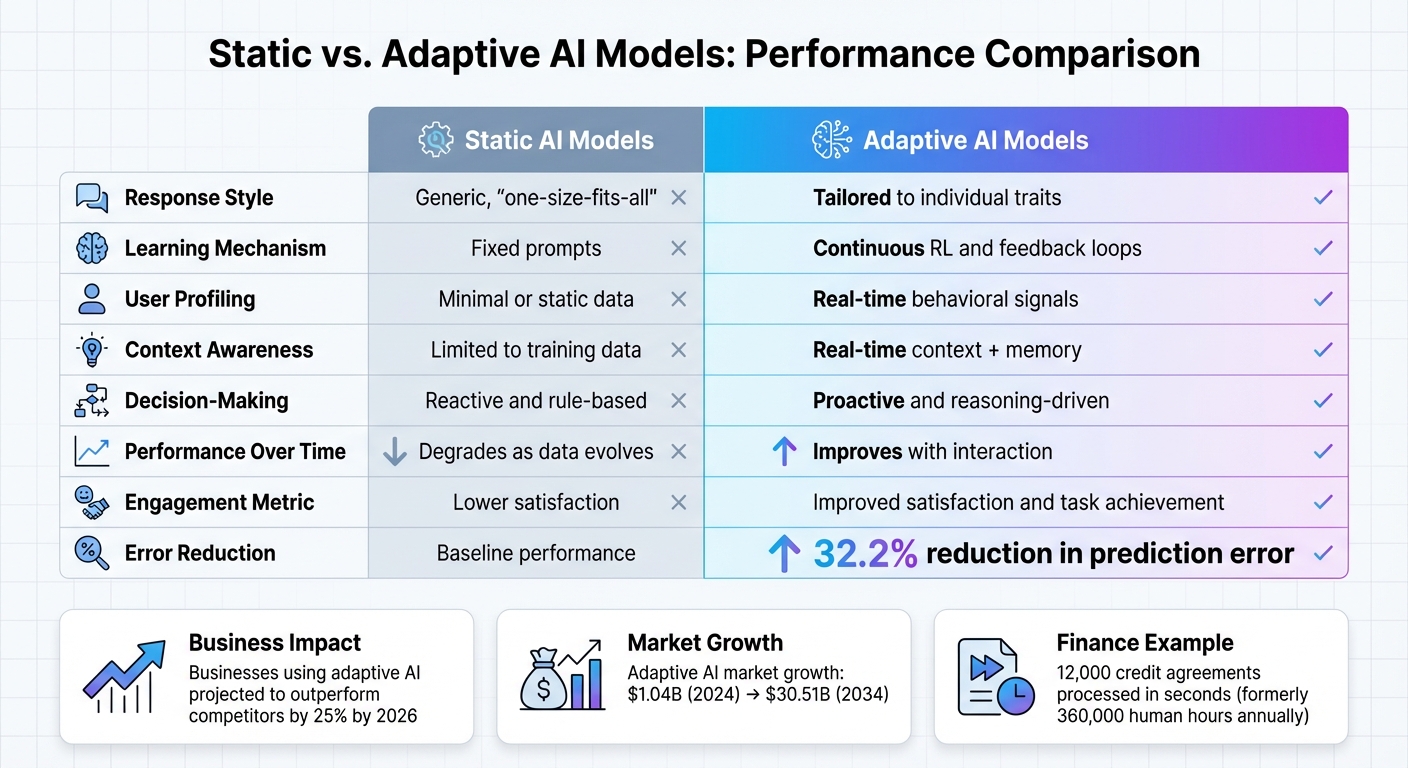
Static vs. Adaptive AI Responses
The contrast between static and adaptive AI models highlights the advantages of adaptability. Static models operate on fixed prompts or scripts, treating all users the same. They rely solely on explicit queries and lack the ability to personalize responses. As the PsychAdapter Research Team noted:
"The transformers behind these large language models... generate text that represents average patterns... they do not explicitly represent differences in psychological traits."[2]
Adaptive models, on the other hand, analyze behavioral patterns and emotional cues to adjust their strategies in real time. This capability, often referred to as "Bilateral AI", allows these systems to evolve during a single interaction. AI researcher Victoria Reed describes it succinctly:
"Bilateral AI adapts to users."[16]
The benefits of adaptive AI are clear when compared to static systems. Businesses using adaptive AI are projected to outperform competitors by 25% by 2026[15]. In finance, adaptive systems can process 12,000 commercial credit agreements in seconds - tasks that once required 360,000 human hours annually[15]. The global market for adaptive AI is expected to grow from $1.04 billion in 2024 to $30.51 billion by 2034[15].
| Feature | Static AI Models | Adaptive AI Models |
|---|---|---|
| Response Style | Generic, "one-size-fits-all"[12] | Tailored to individual traits[12] |
| Learning Mechanism | Fixed prompts[1] | Continuous RL and feedback loops[12][13] |
| User Profiling | Minimal or static data[1] | Real-time behavioral signals[12][6] |
| Context Awareness | Limited to training data[15] | Real-time context + memory[15] |
| Decision-Making | Reactive and rule-based[15] | Proactive and reasoning-driven[15] |
| Performance Over Time | Degrades as data evolves[15] | Improves with interaction[15] |
| Engagement Metric | Lower satisfaction[12] | Improved satisfaction and task achievement[12] |
| Error Reduction | Baseline performance[13] | 32.2% reduction in prediction error[13] |
Platforms like Personos showcase the potential of adaptive AI. By combining conversational interfaces with dynamic personality insights, Personos offers tools for conflict resolution, team collaboration, and personalized communication coaching. These interactions remain private, visible only to the user, ensuring a balance between personalization and privacy.
Applications in Workplace and Coaching Environments
The way teams collaborate and coaches guide their clients is undergoing a transformation, thanks to real-time personality analysis. Moving from static, annual engagement surveys to dynamic, data-driven monitoring is opening doors to preventing conflicts before they arise and tailoring professional growth to individual needs. These insights are making a noticeable impact on team dynamics and client development in both workplaces and coaching environments.
Conflict Resolution and Team Dynamics
AI has taken conflict resolution to a new level. By analyzing emails, chat logs, and video calls in real time, these systems can spot subtle frictions that traditional surveys often miss. For example, they can predict conflicts up to two weeks in advance by observing changes in communication frequency and emotional tone. This is significant, considering U.S. employees spend an average of 2.8 hours per week managing conflicts - costing businesses around $359 billion annually in paid hours.
Some companies are already seeing results. Restructuring teams based on AI insights has cut meeting times by 30% and improved project delivery rates. Advanced AI can even differentiate between frustration caused by a technical challenge and frustration directed at a colleague, allowing for more precise interventions. One aerospace manufacturer implemented a system that predicted major conflicts with 76% accuracy two weeks ahead of time. Early interventions based on these predictions reduced actual conflicts by 50% [19].
Personos is putting these insights to work by analyzing both individual and group dynamics in the workplace. It provides actionable advice to managers and coaches while maintaining privacy, a critical feature. This is especially relevant since 92% of people report friction with at least one of their team’s core behaviors [18].
Improving Coaching Strategies
AI isn’t just helping in workplaces - it’s also revolutionizing how coaches support their clients. Real-time personality analysis provides a deeper level of personalization that goes beyond traditional intake forms and self-assessments. By reviewing data from prior sessions, AI can create detailed client profiles and narratives, uncovering patterns clients might not see themselves. It even enables role-playing with virtual alter egos, offering a safe way to explore different scenarios. Additionally, real-time sentiment and voice analysis gives coaches immediate feedback, signaling when to shift their approach based on changes in a client’s tone or emotional state [20].
The impact is measurable. A study from Harvard University showed that consultants using AI completed 12.2% more tasks, worked 25.1% faster, and delivered 40% higher-quality results compared to those who didn’t use AI [21]. Business coach Luisa Zhou highlights this balance between technology and human expertise:
"The future of AI lies in how it complements rather than replaces coaches. Only you have the experience, creativity, and empathy needed to be a great coach." [21]
Platforms like Personos take this further, combining a conversational AI interface with personality insights and psychological assessments such as Enneagram, CliftonStrengths, and MBTI. This allows coaches to fine-tune their strategies in real time. The platform even includes task tracking to ensure that coaching translates into measurable progress [22].
sbb-itb-f8fc6bf
Measuring the Impact of Personality-Driven AI
As AI continues to refine how it communicates, researchers are now able to measure its influence with tangible data. Recent studies show that these systems can deliver measurable improvements in areas like identifying personality types and driving outcomes such as increased engagement and sales.
Engagement and Satisfaction Metrics
A study examining over 57,000 chatbot interactions revealed that aligning a consumer's personality with a matching AI personality significantly boosted both engagement and purchasing outcomes. This effect was particularly strong in scenarios involving social or persuasive goals [23].
The accuracy of personality classification has also seen impressive advancements. For instance, GPT-4 can correctly classify 76% of an individual’s MBTI personality type by analyzing just their 50 most recent tweets. This far surpasses older methods, such as Recurrent Neural Networks, which achieved only 49.75% accuracy [10]. When users interact with AI that mirrors their own personality traits and opinions, they are more likely to perceive the AI as trustworthy, competent, and approachable [3].
"Matching consumer personality with congruent chatbot personality had a positive impact on consumer engagement with chatbots and purchasing outcomes for interactions involving social gain" [23]
Lester Johnson, a researcher from Computers in Human Behavior, highlighted the practical implications of these findings. According to him, personality matching works best in contexts where persuasion, relationship-building, or coaching is the goal, rather than simple tasks like retrieving information.
Beyond engagement, the choice of personality analysis framework plays a key role in ensuring precise communication.
Comparing Personality Analysis Frameworks
Different personality frameworks offer varying levels of accuracy and utility, shaping how effectively AI can communicate. The Big Five (OCEAN) model and MBTI, for example, each have distinct strengths depending on the context. The Big Five is particularly reliable for predicting task performance and fine-tuning persuasive communication, while MBTI is widely used for persona-based interactions and team-building [25][26].
Here’s a closer look at how these frameworks compare:
| Framework | Classification Accuracy | Primary Impact on Communication | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Five (OCEAN) | 87.33% – 94.5% (Generation Accuracy) [2] | Offers nuanced insights into traits like neuroticism and extraversion | Clinical training, personalized assistants, mental health |
| MBTI | 73% – 76% (Classification Accuracy) [10] | Categorizes users into 16 types for resonance and micro-targeting | Team dynamics, coaching, professional development |
| Interpersonal Circumplex | High (via rotation of Big Five) [2] | Maps communication along "Warmth" and "Dominance" axes | Social behavior modeling, interpersonal motive analysis |
Instruction-tuned models, such as Flan-PaLM 540B, demonstrate internal consistency scores in the mid-to-high 0.90s, significantly outperforming base models [24]. This level of reliability ensures that AI can adapt its communication style in ways that feel genuine and useful to users. Tools like Personos leverage these frameworks to provide coaches and managers with actionable insights, helping them craft communication strategies that resonate on a deeper level.
Future Directions for AI and Personality Adaptation
The next wave of AI development isn't just about completing tasks - it’s about understanding the emotional nuances of human conversation. Researchers are diving into Affective Reinforcement Learning, a method that trains AI not for rigid, rule-based tasks like solving equations but for emotionally attuned, personality-sensitive interactions. As Naifan Zhang and colleagues explain:
"This work establishes a new frontier for RL: optimizing models for the deeply subjective, deeply human dimensions of conversation" – Naifan Zhang et al. [6].
One exciting breakthrough is the rise of General User Models (GUM), which analyze unstructured computer interactions - like screenshots, file usage, and app behavior - to grasp a user’s preferences, knowledge, and intent. In May 2025, Stanford researchers introduced "Gumbo", a proactive assistant that monitored screen activity over five days. For instance, Gumbo spotted a wedding invitation in a message thread and suggested an affordable suit rental. In other cases, it helped users by designing research frameworks or creating personalized moving plans based on relocation-related tasks. Impressively, Gumbo achieved 100% accuracy on high-confidence tasks and maintained an average accuracy of 76.15% across all its inferences [27].
On the technical side, tools like PsychAdapters and Profile-LLM are making personality adaptation more precise and flexible. PsychAdapters embed psychological traits directly into AI's transformer layers, while Profile-LLM allows for adjustable personality intensity. This dynamic approach lets AI fine-tune its behavior in real time, adapting to users' emotional states and shifting preferences instead of sticking to static, pre-defined personas [1]. These advancements are paving the way for AI that feels more human and responsive.
However, challenges remain. Smaller on-device models often struggle to handle complex personality traits, and maintaining large context windows demands significant computational resources [1][28]. Privacy concerns are also shaping the direction of this research, with a growing focus on on-device adaptation, where user data remains securely stored on local hardware. As researcher Omar Shaikh notes:
"GUMs allow a user to construct a private, computational representation of their own behavior, knowledge, beliefs, and preferences by feeding unstructured observations through an inference architecture" [27].
This privacy-conscious approach is already being applied in tools like Personos, which provide managers and coaches with personality insights while keeping user data secure. These tools offer actionable strategies for communication without compromising privacy.
Looking ahead, technologies like Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and quantum computing could take personalization to the next level. By interpreting neural signals and emotional states directly, these systems could anticipate user needs before they’re even expressed [14][29]. The future of AI lies in creating assistants that don’t just adapt to personality types but proactively discover and act on user needs based on observed context. It’s a shift from reactive to proactive assistance, promising a more intuitive and seamless user experience.
Conclusion
AI-powered personality insights are reshaping how we communicate, collaborate, and grow in the workplace. By accurately identifying personality traits and adapting communication styles in real time, these systems deliver tangible results. For instance, IBM's Career Coach saved over $100 million by reducing employee turnover, and Workday's internal gig program achieved an impressive 95% skill development rate [2][5]. These examples highlight the growing impact of AI in driving workplace success.
The benefits are clear: employees report a 158% boost in engagement when using productivity-enhancing technology, and 71% now expect personalized interactions as part of their work experience [5]. Jim Link, CHRO at SHRM, emphasizes the importance of this shift:
"Personalized career development is one of the most impactful ways to improve retention. AI-powered career pathing and internal gig marketplaces help employees see a future within the company" [5].
Tools like Personos are leading this charge, offering real-time personality analysis and tailored communication strategies that improve team dynamics, resolve conflicts, and encourage individual growth. These platforms combine actionable insights with strong data privacy safeguards, delivering the kind of personalized guidance that once required extensive one-on-one coaching.
Looking ahead, AI systems will continue to evolve, anticipating needs while maintaining a commitment to user privacy. By helping us understand personality - both our own and others’ - AI is not just advancing technology; it’s creating practical solutions for stronger teams, better leadership, and healthier workplace relationships.
FAQs
How does AI analyze personality traits using the Big Five model?
AI taps into the Big Five (OCEAN) model to assess personality traits by analyzing how people communicate in real time. Through natural language processing (NLP), it evaluates elements like word choice, sentence structure, tone, and sentiment. These insights are then mapped to the five core dimensions: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism.
Machine learning algorithms, trained on extensive datasets such as personality assessments, process these communication cues to create dynamic personality profiles. Tools like Personos utilize this technology to adjust communication strategies on the fly, offering features like personalized prompts, conflict resolution advice, and detailed team dynamic reports. This approach helps streamline interactions and enhances collaboration in practical, everyday situations.
How does AI benefit from adapting communication styles in real time?
When AI adjusts how it communicates in real time, it creates a more tailored and engaging experience for users. This ability to adapt on the fly brings several clear advantages:
- Better engagement and satisfaction: Conversations become smoother and more meaningful when tailored to a user’s personality, often leading to a greater sense of empathy and usefulness.
- Stronger trust and understanding: Aligning with a user’s communication style reduces misunderstandings and builds a connection, making interactions feel more natural.
- Greater effectiveness: Customizing communication can enhance persuasion, boost confidence in recommendations, and even lead to better outcomes, such as higher conversion rates in marketing.
For businesses, this adaptability turns AI into a valuable partner in areas like coaching, conflict resolution, and team collaboration. Platforms such as Personos analyze personality cues in real time to deliver actionable insights, proactive suggestions, and dynamic reports. This helps teams communicate clearly, resolve conflicts quickly, and stay productive. The result? A workplace where every interaction feels personalized, fostering inclusivity and efficiency.
How does AI protect privacy when analyzing personality data in real time?
AI systems built for personality analysis place a strong emphasis on privacy and security, ensuring user data stays protected while offering real-time insights. These systems are designed to collect only the bare minimum of data needed, anonymize or aggregate sensitive details, and use encryption to secure data both in transit and at rest. They also adhere to strict user consent protocols, transparent data-retention policies, and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Many platforms take it a step further by processing interactions locally whenever possible, sending only anonymized data to cloud services. This approach allows the AI to adjust its communication style without risking exposure of personally identifiable information. Through a combination of minimal data collection, robust encryption, and clear consent practices, these systems ensure that real-time personality analysis respects user privacy while aligning with modern regulatory expectations.